Moodle is a popular, free, and open-source Course Management system based on PHP released under the GNU General Public License.
The Moodle platform is highly customizable and takes a modular approach to features, so it is extensible and adaptable to your needs. It is probably most popular open source learning management platform available today.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Moodle on your Debian 11 OS.
Step 1: Update Operating System
Update and upgrade the system repositories to make sure all existing packages are up to date:
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeStep 2: Install Apache webserver
Apache web server is available on the Debian repository and can be installed via apt package manager by executing the following command:
$ sudo apt install apache2You can start the Apache service and configure it to run on startup by entering the following commands:
$ sudo systemctl start apache2
$ sudo systemctl enable apache2Verify the status of the Apache service using systemctl status command:
$ sudo systemctl status apache2Output:
● apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running)
Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
Process: 459 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/apachectl start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 666 (apache2)
Tasks: 6 (limit: 2301)
Memory: 24.3M
CPU: 439ms
CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service
├─666 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─677 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─678 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─679 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
├─680 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
└─681 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
You can test to make sure everything is working correctly by navigating to:
http://your-IP-addressIf everything is configured properly, you should be greeted by the Apache2 Debian Default Page, as seen below.
Step 3: Install PHP and PHP extensions for Moodle
By default, Debian 11 comes with PHP version 7.4.
You can install PHP and required PHP extensions using the following command:
$ sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-iconv php-intl php-soap php-zip php-curl php-mbstring php-mysql php-gd php-xml php-pspell php-json php-xmlrpcVerify if PHP is installed.
php -vOutput: PHP 7.4.28 (cli) (built: Feb 17 2022 16:17:19) ( NTS )
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v3.4.0, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v7.4.28, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
Step 4: Install MariaDB
We will use MariaDB as the database system for Moodle (Moodle supports MariaDB/MySQL and PostgreSQL).
You can install MariaDB with the following command:
$ sudo apt install mariadb-server mariadb-clientThe commands below can be used to stop, start and enable MariaDB service to start automatically at the next boot:
$ sudo systemctl start mariadb
$ sudo systemctl stop mariadb
$ sudo systemctl enable mariadbAlso, you can verify the status of the MariaDB service using systemctl status command:
$ sudo systemctl status mariadbOutput:
● mariadb.service - MariaDB 10.5.15 database server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running)
Docs: man:mariadbd(8)
https://mariadb.com/kb/en/library/systemd/
Main PID: 16987 (mariadbd)
Status: "Taking your SQL requests now..."
Tasks: 8 (limit: 2287)
Memory: 63.0M
CPU: 1.403s
CGroup: /system.slice/mariadb.service
└─16987 /usr/sbin/mariadbd
Then open the MariaDB default configuration file:
$ sudo nano /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/50-server.cnfUnder ‘[mysqld]‘ line, paste the following configuration:
default_storage_engine = innodb
innodb_file_per_table = 1
innodb_file_format = BarracudaSave and exit, then restart MariaDB service:
$ sudo systemctl restart mariadbStep 5: Create Database
Log into the MariaDB prompt:
$ sudo mysql -u rootTo create a database, database user, and grant all privileges to the database user run the following commands:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE moodledb;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'moodle_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Moodle_Passw0rd!';
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON moodledb.* TO 'moodle_user'@'localhost';
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXITStep 6: Download Moodle
We will now download the latest stable Moodle version from the Moodle Official site.
Use the following command to download Moodle:
$ sudo wget https://download.moodle.org/download.php/direct/stable400/moodle-4.0.1.zipExtract file into the folder /var/www/html/ with the following command:
$ sudo unzip moodle-4.0.1.zip -d /var/www/html/Then, create a new directory in /var/www/html directory:
$ sudo mkdir /var/www/html/moodledataEnable permission for the Apache webserver user to access the files:
$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/moodle/
$ sudo chmod -R 755 /var/www/html/moodle/
$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/moodledata/Step 7: Configure Apache Web Server for Moodle
Navigate to /etc/apache2/sites-available directory and run the following command to create a configuration file for your installation:
$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/moodle.confAdd the following content:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin [email protected]
ServerName your-domain.com
ServerAlias www.your-domain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/moodle
<Directory /var/www/html/moodle/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/your-domain.com_error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/your-domain.com_access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Save the file and Exit.
Enable the virtual host:
$ sudo a2ensite moodle.confAfter that, restart the Apache web server.
$ sudo systemctl restart apache2Step 8: Access Moodle Web Installer
Open your browser type your domain e.g http://your-domain.com You will see the Moodle installation page.
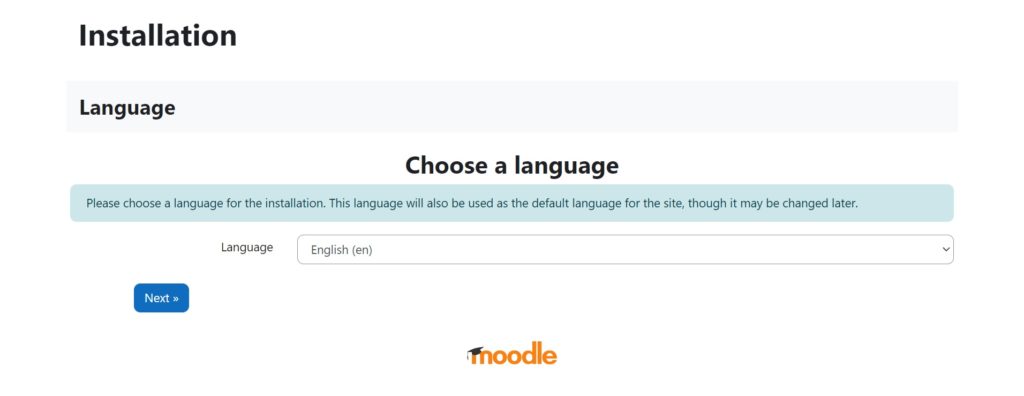
Choose a language, and then click ‘Next‘:
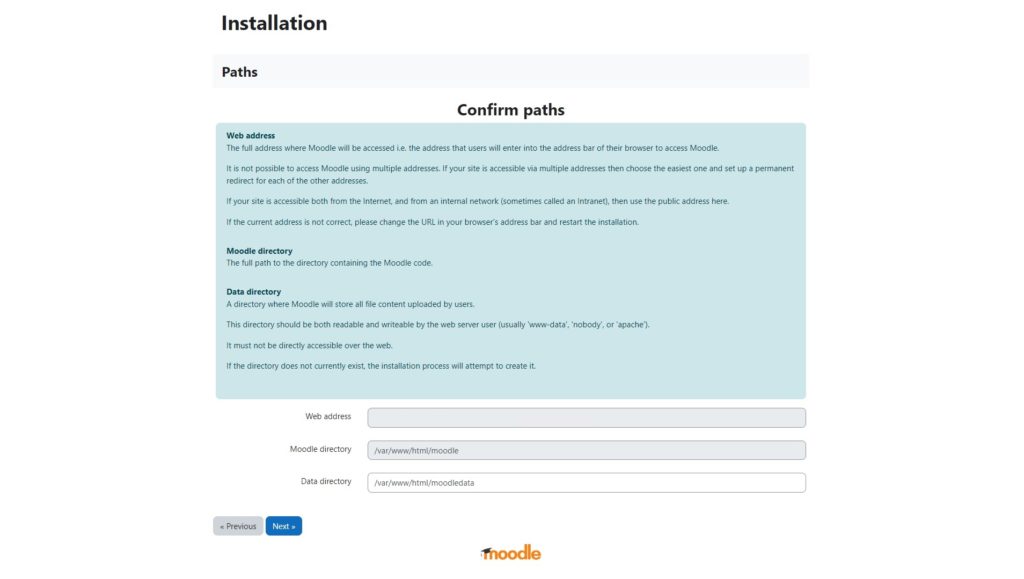
Configure the URL, web root directory, and data directory and then click ‘Next‘:
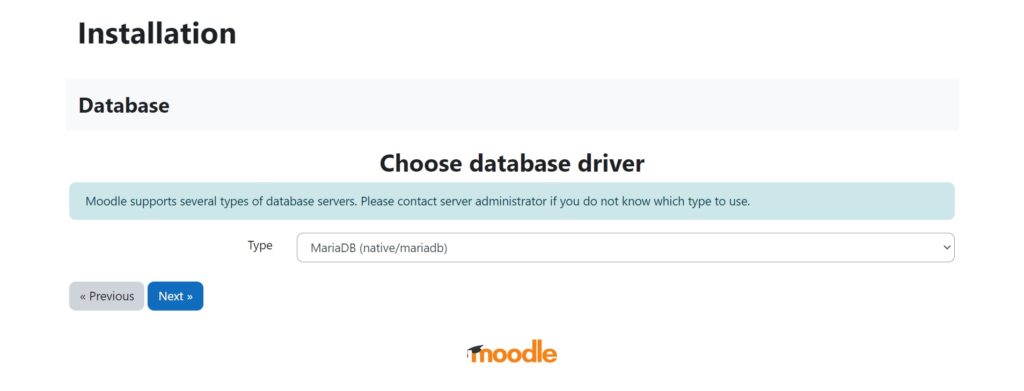
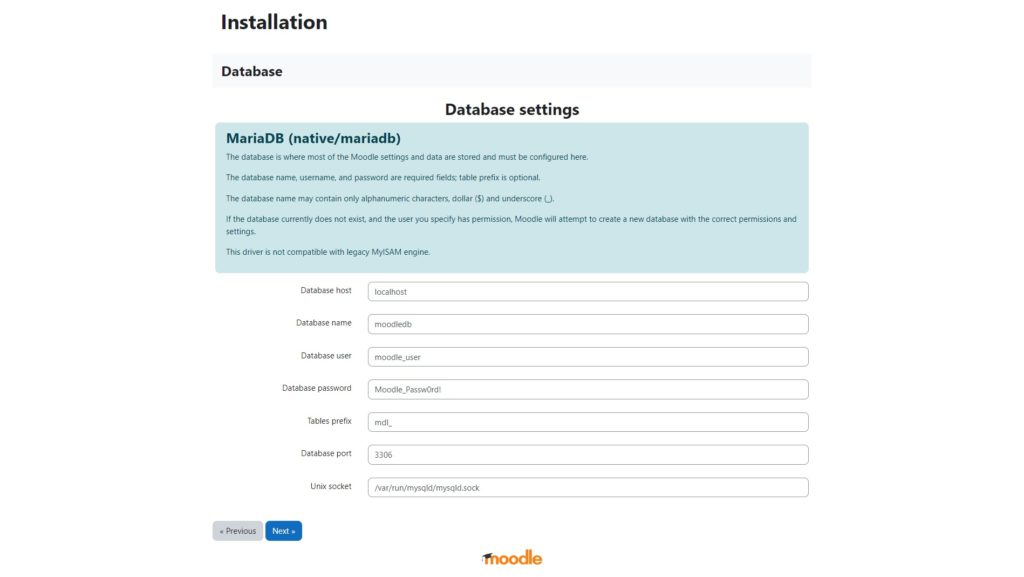
Configure ‘Database driver‘, use MariaDB database server and then click ‘Next‘.
Type in the database information and then click ‘Next‘ to continue.
Accept the Copyright Agreement. Just click ‘Continue‘.

System Checking, checks the server configuration and all PHP extensions needed by Moodle.
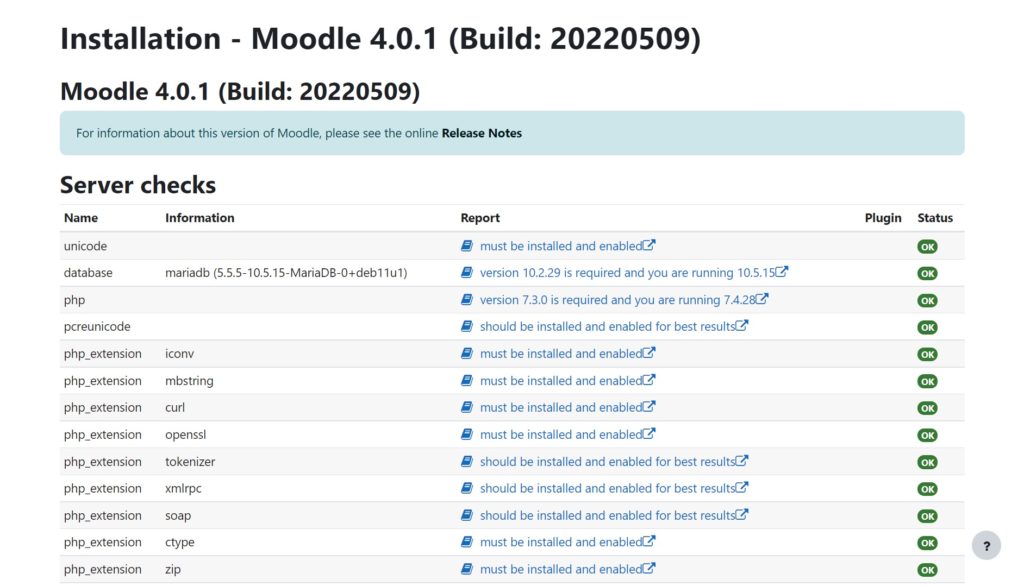
If all the requirements are OK click ‘Continue’

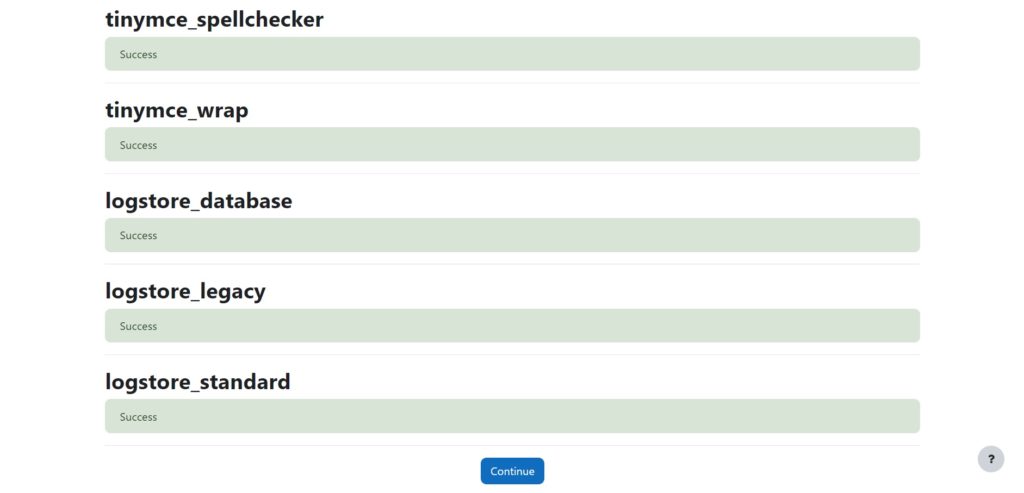
Make sure all results are ‘Success‘. Then click ‘Continue‘ again.
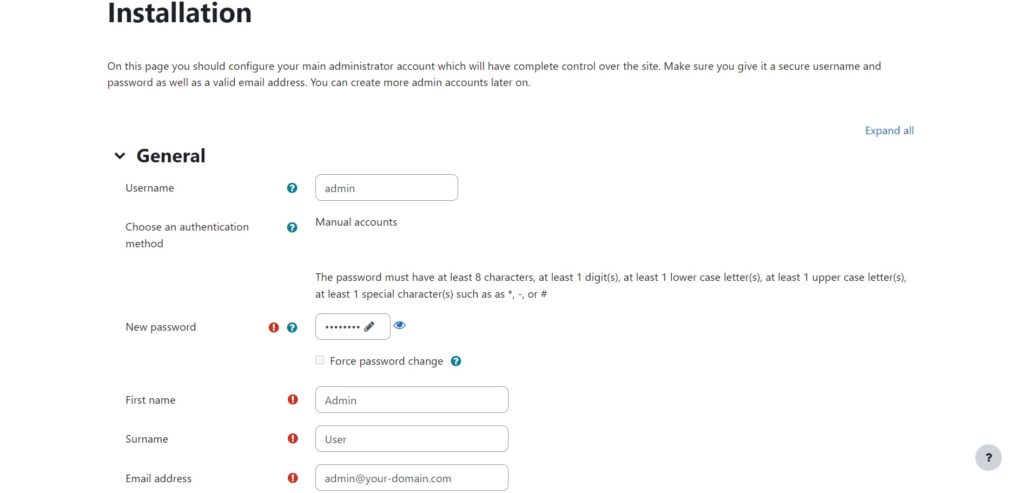
Fill in your admin info and click ‘Update profile‘.
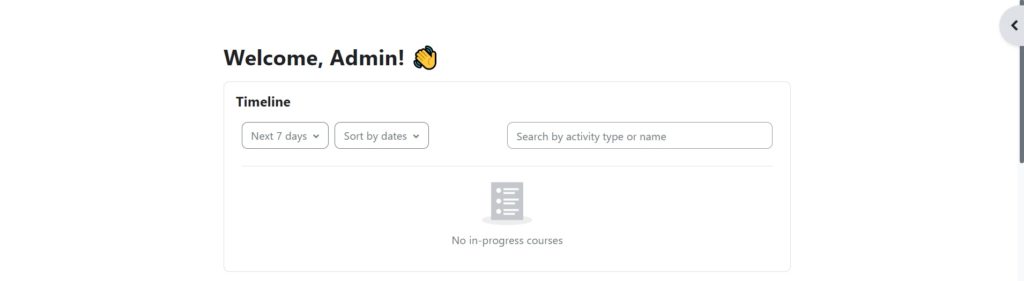
You will be redirected to the user admin ‘Dashboard‘:
Comments and Conclusion
That’s it. You have successfully installed Moodle on Debian 11 OS.
If you have any questions please leave a comment below.


This tutorial is among the best I’ve found on internet with no gaps or pitfalls. I would recomend to include how to use php with fpm instead of apache2