RainLoop is an open-source web-based email client that allows users to access their email accounts through a web browser. It provides a user-friendly interface for managing emails, contacts, and other related tasks without the need for a dedicated email client like Outlook or Thunderbird.
It is designed to be lightweight, fast, and easy to install, making it a popular choice for those who want a simple webmail solution.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install RainLoop on Debian 12 OS with Nginx web server and MariaDB database server..
Step 1: Update Operating System
Update your Debian 12 operating system to the latest version with the following command:
# apt update && apt upgradeAlso, install necessary packages.
# apt install curl nano wget unzip zipStep 2: Install Nginx webserver
You can install it via apt package manager by executing the following command.
# apt install nginxVerify the status of the Nginx service using systemctl status command:
# systemctl status nginxStep 3: Install PHP
To install PHP and the necessary extensions, run the following command:
# apt install php php-cli php-fpm php-json php-common php-mysql php-zip php-imap php-mbstring php-curl php-xmlOnce the installation is complete verify if PHP is installed:
php -vOutput:
PHP 8.2.12 (cli) (built: Oct 27 2023 13:00:10) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v4.2.12, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.2.12, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
After installing all the packages, edit the php.ini file:
# nano /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.iniChange the following settings per your requirements:
max_execution_time = 300
memory_limit = 512M
post_max_size = 25M
upload_max_filesize = 25MTo implement the changes, restart the php-fpm service:
# systemctl restart php8.2-fpmStep 4: Install MariaDB and create a database
To install MariaDB run the following command:
# apt install mariadb-server mariadb-clientVerify the status of the MariaDB service using systemctl status command:
# systemctl status mariadbBy default, MariaDB is not hardened. You can secure MariaDB using the mysql_secure_installation script.
# mysql_secure_installationConfigure it like this:
- Set root password? [Y/n] Y
- Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y
- Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y
- Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y
- Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] YNow run the command below to log in to the MariaDB shell.
# mysql -u root -pOnce you are logged in to your database server you need to create a database for the Roundcube installation:
mysql> CREATE DATABASE rainloop;
mysql> CREATE USER 'rainloopuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Str0ngPa$$word';
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON rainloop . * TO 'rainloopuser'@'localhost';
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
mysql> exit;Step 5: Download RainLoop
You can download the latest stable release version for RainLoop with the following command:
# https://www.rainloop.net/repository/webmail/rainloop-latest.zipAfter that, you will need to decompress the RainLoop archive:
# unzip rainloop-latest.zip -d /var/www/rainloop/Make Nginx the owner of the rainloop folder and grant it sufficient permissions.
# chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/rainloop
# chmod 755 -R /var/www/rainloopStep 6: Configure Nginx for RainLoop
Then, create an virtual host configuration file:
# nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/rainloop.confAdd the following lines:
server {
listen 80;
server_name webmail.your-domain.com;
root /var/www/rainloop;
index index.php;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(.*)$;
fastcgi_keep_conn on;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
location ^~ /data {
deny all;
}
}
Save and exit the configuration file.
Check Nginx syntax:
# /usr/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
To implement the changes, restart Nginx webserver:
# systemctl restart nginxStep 7: Install free Let’s Encrypt SSL certificate
First we need to install the Certbot client which is used to create Let’s Encrypt certificates:
# apt install certbot python3-certbot-nginxTo get the SSL certificate using the Certbot, type the command given below:
# certbot --nginx -d webmail.your-domain.comIf the SSL certificate is successfully obtained, certbot displays a message to show the configuration was successful:
IMPORTANT NOTES:
- Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/webmail.your-domain.com/fullchain.pem
Your key file has been saved at:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/webmail.your-domain.com/privkey.pem
Your cert will expire on 2024-03-06. To obtain a new or tweaked
version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot
again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
"certbot renew"
- Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
- If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-leNow, you have successfully installed SSL on your website.
Step 8: RainLoop Setup and Configurations
Now open your web browser and go to https://webmail.your-domain.com/?admin and you will see the following screen:
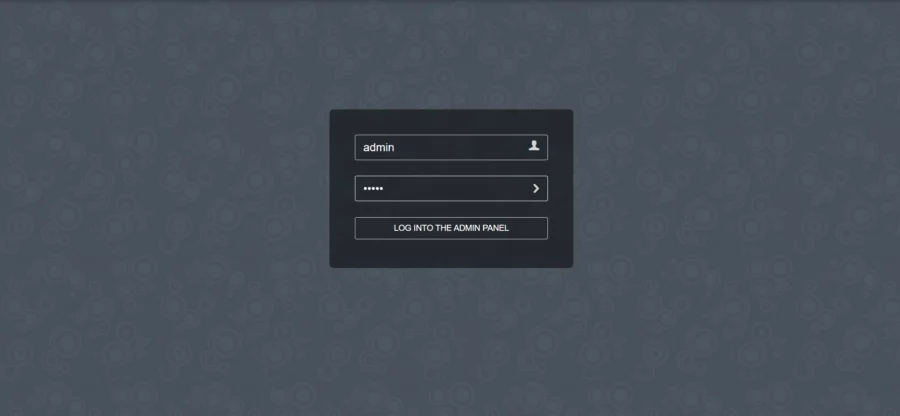
You can log in with the default username admin and default password 12345
You will see the Rainloop dashboard as below:
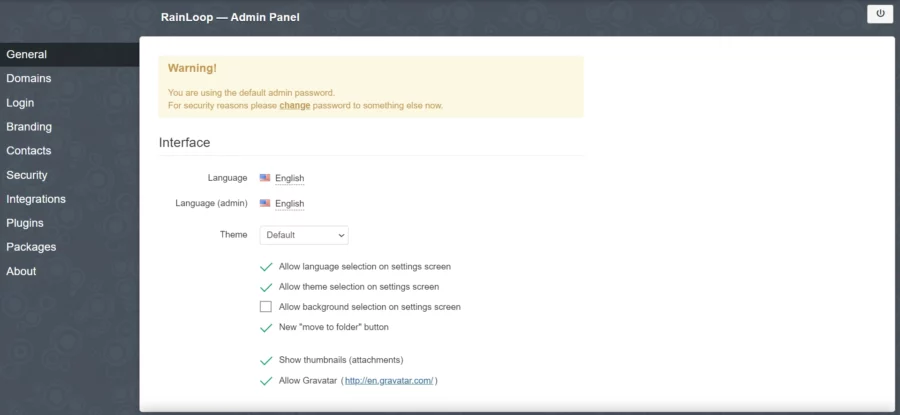
When you login for the first time, you need to change your admin password immediately.
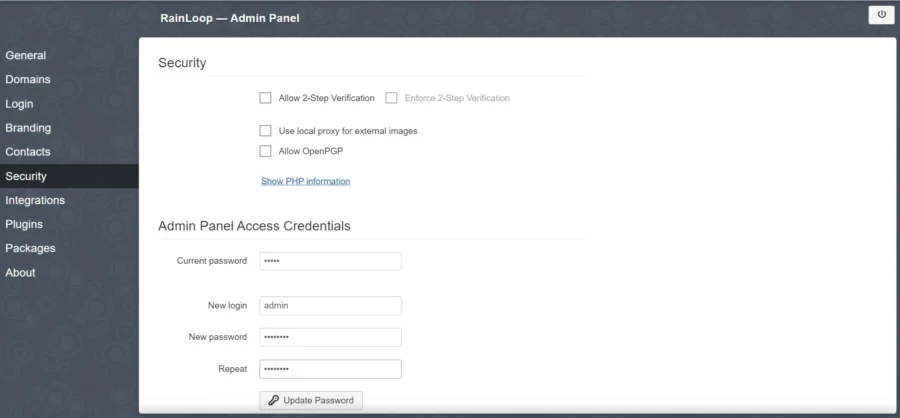
Enter your new password and click on the Update Password button to change the password.
Then, open the Contacts menu and select MySQL from the dropdown menu:
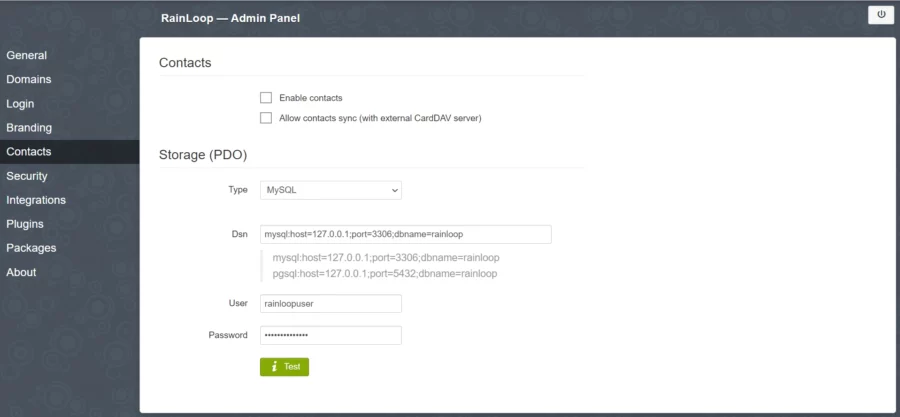
Enter the database credentials you created earlier and press the Test button to check the connection and install the necessary tables.
If the button turns green, it means the connection is successful.
Comments and Conclusion
Congratulations. You have learned how to install RainLoop on Debian 12 OS.
For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official RainLoop documentation.

