Laravel is a free, open-source PHP web application framework used for web development. It follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architectural pattern and provides an elegant syntax and tools for tasks such as routing, templating, authentication, and more. Laravel aims to make web development tasks more enjoyable and efficient by providing a clean and expressive syntax, along with a set of conventions and tools for common tasks.
Laravel has gained popularity in the PHP development community due to its elegant syntax, developer-friendly features, and active community. It is widely used for building web applications, APIs, and various other web-based projects.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Laravel on Debian 12 OS with Nginx web server and MariaDB database server.
Step 1: Update Operating System
The first step is to ensure that your system is up-to-date. You can do this by running the following command:
# apt update && apt upgradeAlso, install necessary packages.
# apt install sudo nano wget unzip zipStep 2: Install Nginx Web Server
To install Nginx web server, run the following command:
# apt install nginxYou can start the Nginx service and configure it to run on startup by entering the following commands:
# systemctl start nginx
# systemctl enable nginxVerify the status of the Nginx service using systemctl status command:
# systemctl status nginxStep 3: Install PHP and PHP extensions
To install PHP and additional PHP modules to support Laravel, run the following command:
# apt install php php-cli php-common php-json php-gmp php-fpm php-xmlrpc php-bcmath php-imagick php-curl php-zip php-gd php-mysql php-xml php-mbstring php-xmlrpc php-intlVerify if PHP is installed.
# php -vOutput:
PHP 8.2.7 (cli) (built: Jun 9 2023 19:37:27) (NTS)
Copyright (c) The PHP Group
Zend Engine v4.2.7, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies
with Zend OPcache v8.2.7, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
After installing all the packages, edit the php.ini file:
# nano /etc/php/8.2/fpm/php.iniChange the following settings per your requirements:
max_execution_time = 300
memory_limit = 512M
post_max_size = 128M
upload_max_filesize = 128M
date.timezone = America/ChicagoTo implement the changes, restart the php-fpm service:
# systemctl restart php8.2-fpmStep 4: Install MariaDB and create a database
You can install MariaDB with the following command:
# apt install mariadb-server mariadb-clientStart the database server daemon, and also enable it to start automatically at the next boot with the following commands:
# systemctl start mariadb
# systemctl enable mariadbOnce the database server is installed, log into the MariaDB prompt:
# mysql -u rootTo create a database, database user, and grant all privileges to the database user run the following commands:
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE laravel_db;
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE USER 'laravel_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Str0ngPa$$word';
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON laravel_db.* TO 'laravel_user'@'localhost';
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> EXITStep 5: Install Composer dependency manager
To install Composer, run the following commands:
# curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php
# mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composerVerify that Composer has been installed successfully by running the following command:
# composer --version
Composer version 2.5.8 2023-06-09 17:13:21Step 6: Install Laravel
Navigate to the webroot directory, type:
# cd /var/www/htmlNow, install Laravel using the composer command, type:
# composer create-project laravel/laravel laravelappThe command creates a new directory called laravelapp and installs all the files and directories for Laravel.
Change the ownership of the Laravel directory to the webserver user and also the permissions:
# chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/laravelapp
# chmod -R 775 /var/www/html/laravelapp/storageOnce the installation is done navigate to the installation directory and check the Laravel version:
# cd laravelapp# php artisanStep 7: Configure Nginx Web Server for Laravel
Navigate to /etc/nginx/conf.d directory and run the following command to create a configuration file:
# nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/laravel.confAdd the following content:
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name your-domain.com;
root /var/www/html/laravelapp/public;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN";
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff";
index index.php;
charset utf-8;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$query_string;
}
location = /favicon.ico { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
location = /robots.txt { access_log off; log_not_found off; }
error_page 404 /index.php;
location ~ \.php$ {
fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $realpath_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
location ~ /\.(?!well-known).* {
deny all;
}
}
Save the file and Exit.
Check Nginx syntax:
# /usr/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
To implement the changes, restart Nginx webserver:
# systemctl restart nginxStep 8: Access your Laravel Application
Open your browser and type your domain e.g http://your-domain.com
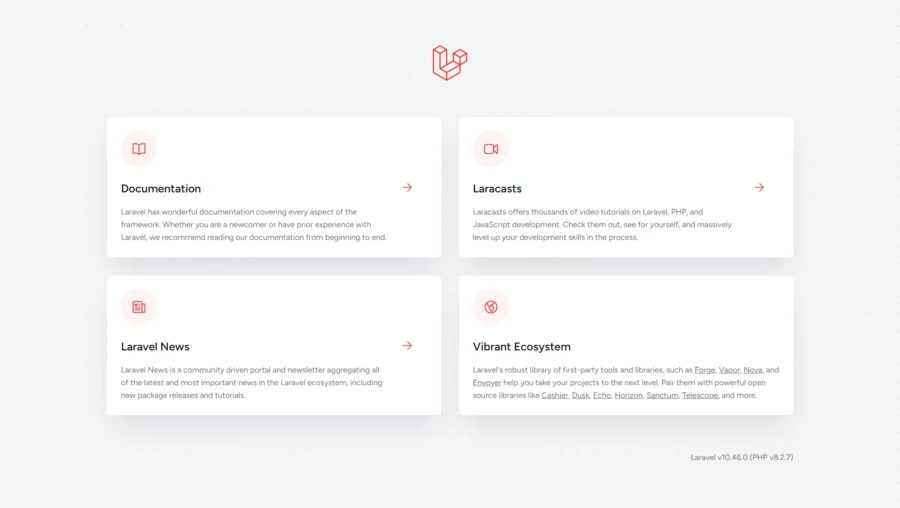
Comments and Conclusion
That’s it. You have successfully installed Laravel on Debian 12.
For additional help or useful information, we recommend you to check the official Laravel documentation.
If you have any questions please leave a comment below.

